
 Did you know that you can grow vegetables, salads and herbs at home, almost free of cost? You don’t need seeds and you don’t even need a garden! Today we’ll explain how you and your child can help the household with an almost endless supply of potentially free, home-grown fresh produce, all year round. Children will have enormous fun with this amazing activity, whilst learning new skills and gaining important knowledge along the way. Even better — you all get to eat the produce once the home-grown ‘crops’ are ready! And it should save money for the household.
Did you know that you can grow vegetables, salads and herbs at home, almost free of cost? You don’t need seeds and you don’t even need a garden! Today we’ll explain how you and your child can help the household with an almost endless supply of potentially free, home-grown fresh produce, all year round. Children will have enormous fun with this amazing activity, whilst learning new skills and gaining important knowledge along the way. Even better — you all get to eat the produce once the home-grown ‘crops’ are ready! And it should save money for the household.
Home-Grown Vegetables & Herbs For Free? How?
 One of the many beauties of this activity is that you don’t need to buy any seeds or plants specifically for the task. You are going to show your child how to regrow small off-cuts of vegetables and herbs that you would already have bought as part of your weekly shop. To explain, some of the parts that you’d normally discard can actually be used to grow new vegetables — lettuce, for example. And, for herbs, there’s an easy and free way to grow new plants from small cuttings of shop-bought herbs that you may have purchased anyway (basil or parsley, for example). Using this approach, you could grow your own vegetables, salads and herbs and, in theory, never have to buy any again! We’ll explain later, in more detail. First, we’ll look at what you and your child will need for your plants to grow in.
One of the many beauties of this activity is that you don’t need to buy any seeds or plants specifically for the task. You are going to show your child how to regrow small off-cuts of vegetables and herbs that you would already have bought as part of your weekly shop. To explain, some of the parts that you’d normally discard can actually be used to grow new vegetables — lettuce, for example. And, for herbs, there’s an easy and free way to grow new plants from small cuttings of shop-bought herbs that you may have purchased anyway (basil or parsley, for example). Using this approach, you could grow your own vegetables, salads and herbs and, in theory, never have to buy any again! We’ll explain later, in more detail. First, we’ll look at what you and your child will need for your plants to grow in.
No Garden Needed?
As we mentioned above, you do not need a garden or greenhouse for this activity. As a minimum, all you need is a windowsill that gets lots of natural light. During warmer months, of course, a balcony or small outdoor patio or space will allow the activity to spread out and bigger volumes to be grown, but it’s really not essential. In any case, keeping to a windowsill means there’s less likelihood of garden pests eating the produce.
 If your household already has flower pots or seed trays, then great. If not, there’s not even any need to buy them if you simply recycle things like empty egg cartons, used yoghurt pots, margarine tubs, the plastic trays from ready meals and suchlike. So long as they’ll hold some earth/compost and some holes are pierced in the bottom for drainage (this is best if done by an adult, for safety), then you’re almost good to go.
If your household already has flower pots or seed trays, then great. If not, there’s not even any need to buy them if you simply recycle things like empty egg cartons, used yoghurt pots, margarine tubs, the plastic trays from ready meals and suchlike. So long as they’ll hold some earth/compost and some holes are pierced in the bottom for drainage (this is best if done by an adult, for safety), then you’re almost good to go.
The only things you might need to spend a few pounds on, just to get going, are:
- Some compost (or use suitably fine, sieved earth, ideally from natural compost, sourced from outdoors if you want to save money). If buying new, choose peat-free compost as it’s better for the planet. Multi-purpose compost is fine, or seed and cuttings compost will also suit.
- Drip trays to put under your pots or seed trays. These are simply to catch the water and to protect your home. They’re very cheap to purchase. If you’re on a budget, though, you could simply source suitably sized food trays, for instance left over from ready meals, or use existing saucers and suchlike. So long as they catch any draining water from your pots or seed trays and are watertight underneath, they’ll be fine.
Regrowing Vegetables
 Now for the really clever, fun part! Instead of throwing away the ‘root’ part — that you’d normally cut off and discard — from the bottom of vegetables like onions, celery, garlic cloves, beetroot and lettuce, your child should save them, because that’s the part that will regrow if you encourage it. Show your child how to safely cut off and save a section about an inch deep, containing that ‘root’ section, from the bottom of used vegetables from your ordinary, weekly shop. Green onions, spring onions, lemon grass, various types of lettuce, Swiss chard and carrots are all additional examples of vegetables that have this bottom root section that can be harvested for later regrowth. Ginger too, but this takes significantly longer to regrow.
Now for the really clever, fun part! Instead of throwing away the ‘root’ part — that you’d normally cut off and discard — from the bottom of vegetables like onions, celery, garlic cloves, beetroot and lettuce, your child should save them, because that’s the part that will regrow if you encourage it. Show your child how to safely cut off and save a section about an inch deep, containing that ‘root’ section, from the bottom of used vegetables from your ordinary, weekly shop. Green onions, spring onions, lemon grass, various types of lettuce, Swiss chard and carrots are all additional examples of vegetables that have this bottom root section that can be harvested for later regrowth. Ginger too, but this takes significantly longer to regrow.
Once saved, simply place the lower sections, root downwards, into water e.g. in a suitable dish or glass. The depth of the water should be such that the top part is not submerged, but the root section is. Your child should ensure that the water level is maintained during a period of one to three weeks, depending on which type of vegetable it is (they grow at different rates). Some time during this period, visible roots will start to grow. Perhaps increase the depth of water once this happens. Once roots are substantial, the new plants can be transferred to the pots or containers of compost. Ensure that the roots are covered in soil but the upper parts protrude into the air as that part will eventually start to grow too.  The compost should be kept moist as the vegetable regrows into another one that can, again, be harvested to eat as part of a healthy meal.
The compost should be kept moist as the vegetable regrows into another one that can, again, be harvested to eat as part of a healthy meal.
Interestingly, carrot tops (the growing green leaves above the root) can also be harvested for use as ‘greens’ in salads and suchlike. Instead of discarding these, pop the tops in water as above and soon enough you’ll see lots of greens growing.
Regrowing Herb Clippings
 Herbs like basil, coriander, parsley, rosemary are also easy to regrow. When you’ve used most of them from your weekly shop for meals, save a few clippings from left-over stems. Clipping length will be different depending on the herb used. For example, basil clippings should be about 4 inches (100mm) long and rosemary clippings should be 2 to 3 inches (50-75mm) long. You may need to experiment a bit at first, so save a few different lengths if unsure initially.
Herbs like basil, coriander, parsley, rosemary are also easy to regrow. When you’ve used most of them from your weekly shop for meals, save a few clippings from left-over stems. Clipping length will be different depending on the herb used. For example, basil clippings should be about 4 inches (100mm) long and rosemary clippings should be 2 to 3 inches (50-75mm) long. You may need to experiment a bit at first, so save a few different lengths if unsure initially.
In a similar way to the root vegetables above, these clippings need to be dangled and left in water on a windowsill until the roots are a couple of inches (50mm) or so in length. Once again, those can then be transplanted to the pots or containers with compost burying the roots. Again, your child should keep the compost moist until new, substantial herb plants have regrown and are ready again to eat. At this time, the whole process can begin again. Regrowing herbs is a great way to encourage children to try more types of them, to widen their food palettes and preferences.
Growing Seeds from Shop-Bought Vegetables
 Another way to regrow shop-bought vegetables is to see if they have seeds inside. Tomatoes and peppers are great examples of these. So, when you’re next using them up for meals, get your child to save the seeds from things like peppers (you’d normally discard these anyway) and some seeds from a tomato — each one contains many. These too can be used to grow brand new plants and vegetables for next to nothing. It’s a little more advanced and they need more room, though. The best time to harvest tomato seeds is between summer and autumn, then plant them in spring if they’re intended for the garden. Here’s an advanced method of saving tomato seeds.
Another way to regrow shop-bought vegetables is to see if they have seeds inside. Tomatoes and peppers are great examples of these. So, when you’re next using them up for meals, get your child to save the seeds from things like peppers (you’d normally discard these anyway) and some seeds from a tomato — each one contains many. These too can be used to grow brand new plants and vegetables for next to nothing. It’s a little more advanced and they need more room, though. The best time to harvest tomato seeds is between summer and autumn, then plant them in spring if they’re intended for the garden. Here’s an advanced method of saving tomato seeds.
 It’s similar for marrows, courgettes, pumpkins and squashes, although those need significant space (they’ll want to spread out), so may be more suitable outside once they begin to grow significantly.
It’s similar for marrows, courgettes, pumpkins and squashes, although those need significant space (they’ll want to spread out), so may be more suitable outside once they begin to grow significantly.
Whichever seed you choose to grow from repurposed vegetables, they can be spaced out in your compost pots or trays, then lightly dusted with a thin layer of extra compost to stop them washing away when they’re watered. You can cover them with kitchen roll sheets or cling film initially, as it may help them to germinate faster. Once shoots begin to appear, the child can remove the covering and then ensure that the compost is kept moist, but not soggy, while remaining on the windowsill. Once the seedlings have grown bigger, for example after a month, they will need to be transferred to bigger pots and this may have to happen again when they’re even larger. If allowed to grow to full size and looked after, flowers will eventually appear and later those will turn into new vegetables that will ripen, ready to harvest roughly two months after sewing the seeds.
Children Love Natural Growing Activities
 Children will love looking after these living things and seeing them grow or regrow. They will learn so much along the way and will have a great sense of achievement when successful. Once they’ve succeeded in producing something they can eat (… and potentially regrow again) they’ll probably want to do it more and try different things. The result, of course, is also fresh produce, which is rich in vitamins and nutrients and good for family health. Children will have been entertained, they’ll understand nature better and they’ll learn skills like patience and being responsible too. A key lesson is also to learn from mistakes — something we all have to do. What’s more, this natural activity for children may even save money for the household. All in all, it’s a great activity from every perspective.
Children will love looking after these living things and seeing them grow or regrow. They will learn so much along the way and will have a great sense of achievement when successful. Once they’ve succeeded in producing something they can eat (… and potentially regrow again) they’ll probably want to do it more and try different things. The result, of course, is also fresh produce, which is rich in vitamins and nutrients and good for family health. Children will have been entertained, they’ll understand nature better and they’ll learn skills like patience and being responsible too. A key lesson is also to learn from mistakes — something we all have to do. What’s more, this natural activity for children may even save money for the household. All in all, it’s a great activity from every perspective.
Our Childcare Nursery in Willesden, near Harlesden, Kensal Green & Willesden Green
 Treetops Nursery has its own plant growing area for the children to use and this is just one of many wonderful outdoor activities that they can enjoy and learn from at the setting. It is a really popular nursery in Willesden, near Harlesden, Kensal Green and Willesden Green, so places are in demand. To register for a place for your baby, toddler or under-five child, please get in touch and we’ll be delighted to show and tell you more:
Treetops Nursery has its own plant growing area for the children to use and this is just one of many wonderful outdoor activities that they can enjoy and learn from at the setting. It is a really popular nursery in Willesden, near Harlesden, Kensal Green and Willesden Green, so places are in demand. To register for a place for your baby, toddler or under-five child, please get in touch and we’ll be delighted to show and tell you more:

 guidance and links. Your child will fall into one of 4 possible categories:
guidance and links. Your child will fall into one of 4 possible categories: Socio-economic background matters too:
Socio-economic background matters too:
 Breast milk is nature’s totally natural food for newborns and little ones, containing nothing artificial or added.
Breast milk is nature’s totally natural food for newborns and little ones, containing nothing artificial or added. Babies are also more protected against asthma if they have been breastfed.
Babies are also more protected against asthma if they have been breastfed. Breastfeeding a baby reduces the chance of mothers developing Type 2 Diabetes.
Breastfeeding a baby reduces the chance of mothers developing Type 2 Diabetes. Our top 25 benefits of breastfeeding really only scratch the surface. Breastfeeding and breast milk have many more benefits including anything from saving money and being more convenient (nothing needs buying or preparing) to being better for the planet. With breast milk, there’s no packaging to throw away and it’s a totally sustainable food source, direct from nature. Incredible when you think about it.
Our top 25 benefits of breastfeeding really only scratch the surface. Breastfeeding and breast milk have many more benefits including anything from saving money and being more convenient (nothing needs buying or preparing) to being better for the planet. With breast milk, there’s no packaging to throw away and it’s a totally sustainable food source, direct from nature. Incredible when you think about it.
 Last month, we mentioned what a huge topic formula milk is. So, in this post, we thought we’d explore all the different types of milk available to infants in the UK.
Last month, we mentioned what a huge topic formula milk is. So, in this post, we thought we’d explore all the different types of milk available to infants in the UK. Baby and infant formula milk comes ready-made in liquid form or as a powder that needs to be carefully and hygienically made up. The liquid variety is usually the more expensive of the two and needs to be used sooner, due to its shorter shelf life. Whichever is used, labels should be carefully checked to ensure suitability for the age of the particular baby/infant in question.
Baby and infant formula milk comes ready-made in liquid form or as a powder that needs to be carefully and hygienically made up. The liquid variety is usually the more expensive of the two and needs to be used sooner, due to its shorter shelf life. Whichever is used, labels should be carefully checked to ensure suitability for the age of the particular baby/infant in question. Comfort Formula is another type of formula milk based on cows’ milk, but the milk proteins it contains are already partially broken down (partially hydrolysed). It is marketed as being easier for the infant to digest and, as such, a formula milk that will reduce the chance of constipation or colic. However, there is no evidence to back up such claims. It’s suitable from birth but parents should ask for advice from their Health Visitor or midwife before giving their baby this type of milk, and certainly not use it if their infant is allergic to cows’ milk.
Comfort Formula is another type of formula milk based on cows’ milk, but the milk proteins it contains are already partially broken down (partially hydrolysed). It is marketed as being easier for the infant to digest and, as such, a formula milk that will reduce the chance of constipation or colic. However, there is no evidence to back up such claims. It’s suitable from birth but parents should ask for advice from their Health Visitor or midwife before giving their baby this type of milk, and certainly not use it if their infant is allergic to cows’ milk. From the age of 1: your baby can move onto drinking whole pasteurised cows’ milk as their main drink (or alternatively sheeps’ or goats’ milk so long as it’s also pasteurised) as part of a healthy, balanced diet. It should not be given to children before they’re one because it does not contain enough iron.
From the age of 1: your baby can move onto drinking whole pasteurised cows’ milk as their main drink (or alternatively sheeps’ or goats’ milk so long as it’s also pasteurised) as part of a healthy, balanced diet. It should not be given to children before they’re one because it does not contain enough iron.
 More and more parents are bringing up youngsters as vegetarians these days, so we thought we’d put together a rough guide to raising babies, toddlers and preschoolers as vegetarians. When doing so, certain considerations will need to be made, including ensuring that meals are nutritious, containing all the necessary food groups, vitamins and minerals needed by the very young.
More and more parents are bringing up youngsters as vegetarians these days, so we thought we’d put together a rough guide to raising babies, toddlers and preschoolers as vegetarians. When doing so, certain considerations will need to be made, including ensuring that meals are nutritious, containing all the necessary food groups, vitamins and minerals needed by the very young. The good news is that formula milk that’s suitable for vegetarians is available. Parents may ask their midwife or health professional for any recommendations in regard to types or brands, particularly if one formula milk disagrees with the baby. However, whichever brand and type is chosen, the formula milk must be formulated for the baby’s specific age. This is usually obvious on the product label.
The good news is that formula milk that’s suitable for vegetarians is available. Parents may ask their midwife or health professional for any recommendations in regard to types or brands, particularly if one formula milk disagrees with the baby. However, whichever brand and type is chosen, the formula milk must be formulated for the baby’s specific age. This is usually obvious on the product label. From around the age of 6 months, your baby will usually start the process of weaning off of milk and begin to eat solid foods, albeit given in puréed or liquidised form initially. This is when parents then need to be mindful of their child’s nutritional needs and this is even more pertinent when bringing up a child as a vegetarian.
From around the age of 6 months, your baby will usually start the process of weaning off of milk and begin to eat solid foods, albeit given in puréed or liquidised form initially. This is when parents then need to be mindful of their child’s nutritional needs and this is even more pertinent when bringing up a child as a vegetarian. Well, tofu and other soya products will contain good quantities of protein.
Well, tofu and other soya products will contain good quantities of protein. Iron is essential for growing children and can be found in many of the foods mentioned above. That said, it’s worth mentioning that some foods block the absorption of iron. Such foods include tea as well as whole grains and legumes containing ‘phytates’, dairy products containing ‘casein’ and eggs and dairy products that contain particular forms of calcium. The simple solution to many of these is as follows:
Iron is essential for growing children and can be found in many of the foods mentioned above. That said, it’s worth mentioning that some foods block the absorption of iron. Such foods include tea as well as whole grains and legumes containing ‘phytates’, dairy products containing ‘casein’ and eggs and dairy products that contain particular forms of calcium. The simple solution to many of these is as follows:
 Parents, guardians or carers should start brushing children’s teeth the moment teeth first appear, even when it’s only one or two teeth initially showing through. This is typically around the age of six to ten months when, for most babies, the lower incisors are first to appear. It varies enormously, though, with some babies even being born with one or more teeth. For teething babies, of course, you need to be more gentle with brushing than you would be for an older child, because their gums will probably be sore. Hence, there are some guidelines to follow in that regard. That’s exactly where this article comes in as we explain the accepted best practice for brushing infant teeth.
Parents, guardians or carers should start brushing children’s teeth the moment teeth first appear, even when it’s only one or two teeth initially showing through. This is typically around the age of six to ten months when, for most babies, the lower incisors are first to appear. It varies enormously, though, with some babies even being born with one or more teeth. For teething babies, of course, you need to be more gentle with brushing than you would be for an older child, because their gums will probably be sore. Hence, there are some guidelines to follow in that regard. That’s exactly where this article comes in as we explain the accepted best practice for brushing infant teeth. The same general approach can be used for children aged 3 or over, except toddlers may stand, so long as their head can still rest against you so that it’s kept stable and relatively still while brushing takes place. As mentioned in the preceding section, a pea-sized amount of toothpaste can be used for this age group.
The same general approach can be used for children aged 3 or over, except toddlers may stand, so long as their head can still rest against you so that it’s kept stable and relatively still while brushing takes place. As mentioned in the preceding section, a pea-sized amount of toothpaste can be used for this age group. As well as regular brushing of teeth and dentist check-ups, there are many additional measures that can protect children’s teeth. These really all come down to one thing; avoiding added sugar. So …
As well as regular brushing of teeth and dentist check-ups, there are many additional measures that can protect children’s teeth. These really all come down to one thing; avoiding added sugar. So … The more obvious additional health and safety concerns include the following:
The more obvious additional health and safety concerns include the following: This guide was brought to you by the childcare team at
This guide was brought to you by the childcare team at 

 Less likelihood of developing cardiovascular disease including hyperlipidemia1;
Less likelihood of developing cardiovascular disease including hyperlipidemia1; Higher physical activity and physical fitness levels are associated with improved cognitive performance (e.g., concentration, memory) among students.3
Higher physical activity and physical fitness levels are associated with improved cognitive performance (e.g., concentration, memory) among students.3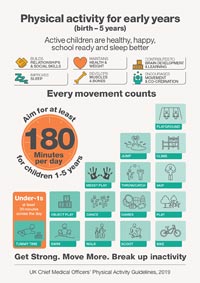
 Knowing how important it is, we take exercise very seriously at Treetops Nursery in Willesden. However, we ensure that it’s always fun and exciting, so that children enjoy it, naturally. Physical movement and active play are all part of
Knowing how important it is, we take exercise very seriously at Treetops Nursery in Willesden. However, we ensure that it’s always fun and exciting, so that children enjoy it, naturally. Physical movement and active play are all part of 
 Equipment and facilities at the nursery are excellent, both indoors and outside. An excellent
Equipment and facilities at the nursery are excellent, both indoors and outside. An excellent  A Good Ofsted Report
A Good Ofsted Report Children’s individual needs, including for those with special needs, are well catered-for at Treetops Nursery, Willesden. In fact, a learning and development programme is tailored to the needs, strengths, weaknesses and interests of each individual child. A ‘Key Person’ is also assigned to each child and this staff member continually monitors their progress, making changes to the tailored programme as appropriate as time goes by. Parents and carers are kept fully informed of children’s progress, including via a journal that is kept for each child. Parents are also free to add notes to the progress journal so a more complete picture is maintained for every child.
Children’s individual needs, including for those with special needs, are well catered-for at Treetops Nursery, Willesden. In fact, a learning and development programme is tailored to the needs, strengths, weaknesses and interests of each individual child. A ‘Key Person’ is also assigned to each child and this staff member continually monitors their progress, making changes to the tailored programme as appropriate as time goes by. Parents and carers are kept fully informed of children’s progress, including via a journal that is kept for each child. Parents are also free to add notes to the progress journal so a more complete picture is maintained for every child.

 Healthy, Balanced Meals for Children
Healthy, Balanced Meals for Children The Benefits of Healthy Eating for Children
The Benefits of Healthy Eating for Children What Should Children be Eating & Drinking?
What Should Children be Eating & Drinking? Portion Sizes
Portion Sizes Healthy Eating at the Nursery
Healthy Eating at the Nursery