
Most people have heard of dyslexia, however the disorder known as dyspraxia is less well known. If you are a parent with children, dyspraxia is something to be aware of, so that you can look out for the possible signs. Today we’ll answer commonly asked questions about the disorder.
Q: What is Dyspraxia?
 A: Dyspraxia is a condition that impairs a person’s ability to fully control motor functions, for example coordinating movement and physical activity. Children with dyspraxia may therefore appear ‘clumsy’. It can be anything from mild to more severe and obviously the mildest variety is hardest for parents to spot. Dyspraxia is classified as a type of Developmental Co-ordination Disorder (‘DCD’) and indeed healthcare professionals may use this terminology for the condition. They may also refer to it as a Specific Developmental Disorder of Motor Function, or ‘SDDMF’ for short.
A: Dyspraxia is a condition that impairs a person’s ability to fully control motor functions, for example coordinating movement and physical activity. Children with dyspraxia may therefore appear ‘clumsy’. It can be anything from mild to more severe and obviously the mildest variety is hardest for parents to spot. Dyspraxia is classified as a type of Developmental Co-ordination Disorder (‘DCD’) and indeed healthcare professionals may use this terminology for the condition. They may also refer to it as a Specific Developmental Disorder of Motor Function, or ‘SDDMF’ for short.
The condition affects four times as many males as it does females and can also sometimes be found in those with ADHD, dyslexia and autism. However, as with dyslexia, dyspraxia has nothing to do with the level of a person’s intelligence.
Q: What Causes Dyspraxia?
 A: Dyspraxia can be something people were simply born with (that’s the developmental kind) or, for others, it was acquired through brain trauma, for example because of an injury or stroke. In this post, however, we’ll concentrate on developmental dyspraxia in relation to children.
A: Dyspraxia can be something people were simply born with (that’s the developmental kind) or, for others, it was acquired through brain trauma, for example because of an injury or stroke. In this post, however, we’ll concentrate on developmental dyspraxia in relation to children.
The reasons for developmental dyspraxia are unclear, however children who were born prematurely or underweight are more prone to the disorder. There is also some evidence to suggest that it can be inherited within families who are prone to the condition. Sadly, children are also more likely to have the disorder if their mothers drank alcohol or took illegal drugs during pregnancy.
Q: What Are the Signs of Dyspraxia?
A: Children with dyspraxia may appear clumsier than their peers. They may also be less naturally good at sport and indeed may even avoid it. Picking up other skills may also be a challenge. Concentration and attention spans can be adversely affected. Following instructions can be a challenge.
Babies may exhibit unusual body positions and have trouble learning to roll or sit. Toddlers under one may adopt strange postures. Infants may be slower at learning to crawl too.
 Children with dyspraxia may also have difficulty:
Children with dyspraxia may also have difficulty:
- independently dressing, buttoning clothes and tying laces;
- walking, jumping, skipping and running;
- using writing instruments to draw and write;
- mastering the use of cutlery to feed themselves;
- catching, kicking and throwing balls;
- stacking objects and playing with some toys;
- carrying out everyday physical tasks and activities in the most appropriate order.
All of this is because they are less able to coordinate movements and physical actions as well as they would without the condition.
One knock-on effect of this is that they may not reach their development milestones as soon as others in their age group. Indeed, this can be an indicator to watch out for. However, DCD/dyspraxia is often hard to diagnose until children are at least 4 to 5 years of age.
Q: What Are the Knock-On Effects of Dyspraxia?
 A: Due to its nature and particularly in regard to its negative effect on sports and active play skills, dyspraxia can lead to children becoming less naturally fit, with all the ramifications that brings.
A: Due to its nature and particularly in regard to its negative effect on sports and active play skills, dyspraxia can lead to children becoming less naturally fit, with all the ramifications that brings.
The effects of dyspraxia can also make children less able to make new friends. This may make them feel a bit left out, ‘different‘ and therefore feel rather isolated. This can, in turn, also lead to lower self-esteem, reduced confidence, frustration and even behavioural problems.
Q: How is Dyspraxia Professionally Diagnosed?
A: If you think your child may be dyspraxic, contact your GP to ensure the problem is not caused by something entirely different. Also liaise with the Special Educational Needs Co-ordinator (‘SENCo’) at your child’s childcare setting, pre-school or school, for advice and support. The GP or SENCo may refer your child to a specialist healthcare professional, for example an occupational therapist and/or paediatrician. Assessment and diagnosis is often carried out by both. Learn more about diagnosing dyspraxia and DCD in children here.
Q: Is there a Cure for Dyspraxia?
A: Although a tiny number of children who are deemed to be a little clumsy may grow out of it, there is no cure for dyspraxia for the vast majority. Some children’s challenges will improve with age, however the earlier symptoms are spotted, the sooner parents, carers, guardians and professionals can help the affected child.
Q: How Can We Help Children with Dyspraxia?
 A: Once diagnosed, tailored help is available for children with dyspraxia/DCD, from a variety of specialists. Support may be needed throughout childhood, including at pre-school and school, to help optimise ability around physical tasks and processes. As every child’s challenges will be unique, a support plan will be customised for each. Support may involve a variety of professionals who will aim to help the child overcome their difficulties as far as possible and to build their confidence, self-esteem, abilities etc. The specialists involved may include paediatric occupational therapists, paediatricians, clinical psychologists, educational psychologists or a mixture of several. All will work in tandem, of course, with childcare professionals, teachers, parents and guardians. Learn more about treatment for dyspraxia here.
A: Once diagnosed, tailored help is available for children with dyspraxia/DCD, from a variety of specialists. Support may be needed throughout childhood, including at pre-school and school, to help optimise ability around physical tasks and processes. As every child’s challenges will be unique, a support plan will be customised for each. Support may involve a variety of professionals who will aim to help the child overcome their difficulties as far as possible and to build their confidence, self-esteem, abilities etc. The specialists involved may include paediatric occupational therapists, paediatricians, clinical psychologists, educational psychologists or a mixture of several. All will work in tandem, of course, with childcare professionals, teachers, parents and guardians. Learn more about treatment for dyspraxia here.
Q: How Does Treetops Nursery Help Dyspraxic Children?
A: As well as looking out for possible first signs of dyspraxia/DCD — and any other disorder — we will work with any specialists to play our part in any tailored support plans for affected children under our care. This may involve task- and process-oriented activities to help children overcome difficulties. As well as working with any guidance from the specialists it will, of course, involve strategic cooperation with parents, carers or guardians involved in the child’s care. In this way, everyone will be working to the same aims, using the same, shared support plans. Our Special Educational Needs Co-Ordinator (‘SENCo’) will also be a crucial part of formulating this plan and, indeed, one of their key roles is to promote equality of opportunity irrespective of any special educational needs or disorders (‘SEND’). In ensuring this, every child achieves personal bests in every area, becoming the very best version of themselves.
Looking for Outstanding Nurseries in Willesden, Near Harlesden, Kensal Green or Willesden Green?
 Treetops Nursery School is a popular nursery and pre-school in Willesden, NW10 (near Harlesden, Kensal Green and Willesden Green). We offer outstanding childcare for babies and children aged up to 5, Monday to Friday. To express an interest, ask a question, book a tour or pre-register for a place, please get in touch:
Treetops Nursery School is a popular nursery and pre-school in Willesden, NW10 (near Harlesden, Kensal Green and Willesden Green). We offer outstanding childcare for babies and children aged up to 5, Monday to Friday. To express an interest, ask a question, book a tour or pre-register for a place, please get in touch:

 Even newborn babies should be encouraged to be active, in order to learn and develop their abilities through interaction and play. At this age, this is achieved largely through activities known collectively as Tummy Time. This is an incredibly important tool for their early development. Tummy Time pretty much describes the essence of the activities — i.e. time spent awake and active on their tummies during their first year.
Even newborn babies should be encouraged to be active, in order to learn and develop their abilities through interaction and play. At this age, this is achieved largely through activities known collectively as Tummy Time. This is an incredibly important tool for their early development. Tummy Time pretty much describes the essence of the activities — i.e. time spent awake and active on their tummies during their first year. It helps them to build physical strength, particularly in their upper body, and helps them achieve various developmental milestones.
It helps them to build physical strength, particularly in their upper body, and helps them achieve various developmental milestones. Another important benefit of Tummy Time is that it helps babies avoid conditions like positional plagiocephaly (otherwise known as ‘flat head syndrome’) and positional torticollis (i.e. a twisted neck) because it allows them to change position more often.
Another important benefit of Tummy Time is that it helps babies avoid conditions like positional plagiocephaly (otherwise known as ‘flat head syndrome’) and positional torticollis (i.e. a twisted neck) because it allows them to change position more often. You can lie the baby on their tummy (while awake of course) on a soft blanket or rug on the floor. Get down low so you can interact with them and play games like peek-a-boo at their level.
You can lie the baby on their tummy (while awake of course) on a soft blanket or rug on the floor. Get down low so you can interact with them and play games like peek-a-boo at their level. Encourage the baby to support their own weight on their hand and arms (almost like a ‘push-up’ kind of position) for short periods. This can initially be done by helping to support them with a hand, lifting them under their chest or tummy. They’ll soon catch on and help to push themselves up and support their own head more and more.
Encourage the baby to support their own weight on their hand and arms (almost like a ‘push-up’ kind of position) for short periods. This can initially be done by helping to support them with a hand, lifting them under their chest or tummy. They’ll soon catch on and help to push themselves up and support their own head more and more.
 guidance and links. Your child will fall into one of 4 possible categories:
guidance and links. Your child will fall into one of 4 possible categories: Socio-economic background matters too:
Socio-economic background matters too:
 Breast milk is nature’s totally natural food for newborns and little ones, containing nothing artificial or added.
Breast milk is nature’s totally natural food for newborns and little ones, containing nothing artificial or added. Babies are also more protected against asthma if they have been breastfed.
Babies are also more protected against asthma if they have been breastfed. Breastfeeding a baby reduces the chance of mothers developing Type 2 Diabetes.
Breastfeeding a baby reduces the chance of mothers developing Type 2 Diabetes. Our top 25 benefits of breastfeeding really only scratch the surface. Breastfeeding and breast milk have many more benefits including anything from saving money and being more convenient (nothing needs buying or preparing) to being better for the planet. With breast milk, there’s no packaging to throw away and it’s a totally sustainable food source, direct from nature. Incredible when you think about it.
Our top 25 benefits of breastfeeding really only scratch the surface. Breastfeeding and breast milk have many more benefits including anything from saving money and being more convenient (nothing needs buying or preparing) to being better for the planet. With breast milk, there’s no packaging to throw away and it’s a totally sustainable food source, direct from nature. Incredible when you think about it.
 Last month, we mentioned what a huge topic formula milk is. So, in this post, we thought we’d explore all the different types of milk available to infants in the UK.
Last month, we mentioned what a huge topic formula milk is. So, in this post, we thought we’d explore all the different types of milk available to infants in the UK. Baby and infant formula milk comes ready-made in liquid form or as a powder that needs to be carefully and hygienically made up. The liquid variety is usually the more expensive of the two and needs to be used sooner, due to its shorter shelf life. Whichever is used, labels should be carefully checked to ensure suitability for the age of the particular baby/infant in question.
Baby and infant formula milk comes ready-made in liquid form or as a powder that needs to be carefully and hygienically made up. The liquid variety is usually the more expensive of the two and needs to be used sooner, due to its shorter shelf life. Whichever is used, labels should be carefully checked to ensure suitability for the age of the particular baby/infant in question. Comfort Formula is another type of formula milk based on cows’ milk, but the milk proteins it contains are already partially broken down (partially hydrolysed). It is marketed as being easier for the infant to digest and, as such, a formula milk that will reduce the chance of constipation or colic. However, there is no evidence to back up such claims. It’s suitable from birth but parents should ask for advice from their Health Visitor or midwife before giving their baby this type of milk, and certainly not use it if their infant is allergic to cows’ milk.
Comfort Formula is another type of formula milk based on cows’ milk, but the milk proteins it contains are already partially broken down (partially hydrolysed). It is marketed as being easier for the infant to digest and, as such, a formula milk that will reduce the chance of constipation or colic. However, there is no evidence to back up such claims. It’s suitable from birth but parents should ask for advice from their Health Visitor or midwife before giving their baby this type of milk, and certainly not use it if their infant is allergic to cows’ milk. From the age of 1: your baby can move onto drinking whole pasteurised cows’ milk as their main drink (or alternatively sheeps’ or goats’ milk so long as it’s also pasteurised) as part of a healthy, balanced diet. It should not be given to children before they’re one because it does not contain enough iron.
From the age of 1: your baby can move onto drinking whole pasteurised cows’ milk as their main drink (or alternatively sheeps’ or goats’ milk so long as it’s also pasteurised) as part of a healthy, balanced diet. It should not be given to children before they’re one because it does not contain enough iron.
 More and more parents are bringing up youngsters as vegetarians these days, so we thought we’d put together a rough guide to raising babies, toddlers and preschoolers as vegetarians. When doing so, certain considerations will need to be made, including ensuring that meals are nutritious, containing all the necessary food groups, vitamins and minerals needed by the very young.
More and more parents are bringing up youngsters as vegetarians these days, so we thought we’d put together a rough guide to raising babies, toddlers and preschoolers as vegetarians. When doing so, certain considerations will need to be made, including ensuring that meals are nutritious, containing all the necessary food groups, vitamins and minerals needed by the very young. The good news is that formula milk that’s suitable for vegetarians is available. Parents may ask their midwife or health professional for any recommendations in regard to types or brands, particularly if one formula milk disagrees with the baby. However, whichever brand and type is chosen, the formula milk must be formulated for the baby’s specific age. This is usually obvious on the product label.
The good news is that formula milk that’s suitable for vegetarians is available. Parents may ask their midwife or health professional for any recommendations in regard to types or brands, particularly if one formula milk disagrees with the baby. However, whichever brand and type is chosen, the formula milk must be formulated for the baby’s specific age. This is usually obvious on the product label. From around the age of 6 months, your baby will usually start the process of weaning off of milk and begin to eat solid foods, albeit given in puréed or liquidised form initially. This is when parents then need to be mindful of their child’s nutritional needs and this is even more pertinent when bringing up a child as a vegetarian.
From around the age of 6 months, your baby will usually start the process of weaning off of milk and begin to eat solid foods, albeit given in puréed or liquidised form initially. This is when parents then need to be mindful of their child’s nutritional needs and this is even more pertinent when bringing up a child as a vegetarian. Well, tofu and other soya products will contain good quantities of protein.
Well, tofu and other soya products will contain good quantities of protein. Iron is essential for growing children and can be found in many of the foods mentioned above. That said, it’s worth mentioning that some foods block the absorption of iron. Such foods include tea as well as whole grains and legumes containing ‘phytates’, dairy products containing ‘casein’ and eggs and dairy products that contain particular forms of calcium. The simple solution to many of these is as follows:
Iron is essential for growing children and can be found in many of the foods mentioned above. That said, it’s worth mentioning that some foods block the absorption of iron. Such foods include tea as well as whole grains and legumes containing ‘phytates’, dairy products containing ‘casein’ and eggs and dairy products that contain particular forms of calcium. The simple solution to many of these is as follows:
 Parents, guardians or carers should start brushing children’s teeth the moment teeth first appear, even when it’s only one or two teeth initially showing through. This is typically around the age of six to ten months when, for most babies, the lower incisors are first to appear. It varies enormously, though, with some babies even being born with one or more teeth. For teething babies, of course, you need to be more gentle with brushing than you would be for an older child, because their gums will probably be sore. Hence, there are some guidelines to follow in that regard. That’s exactly where this article comes in as we explain the accepted best practice for brushing infant teeth.
Parents, guardians or carers should start brushing children’s teeth the moment teeth first appear, even when it’s only one or two teeth initially showing through. This is typically around the age of six to ten months when, for most babies, the lower incisors are first to appear. It varies enormously, though, with some babies even being born with one or more teeth. For teething babies, of course, you need to be more gentle with brushing than you would be for an older child, because their gums will probably be sore. Hence, there are some guidelines to follow in that regard. That’s exactly where this article comes in as we explain the accepted best practice for brushing infant teeth. The same general approach can be used for children aged 3 or over, except toddlers may stand, so long as their head can still rest against you so that it’s kept stable and relatively still while brushing takes place. As mentioned in the preceding section, a pea-sized amount of toothpaste can be used for this age group.
The same general approach can be used for children aged 3 or over, except toddlers may stand, so long as their head can still rest against you so that it’s kept stable and relatively still while brushing takes place. As mentioned in the preceding section, a pea-sized amount of toothpaste can be used for this age group. As well as regular brushing of teeth and dentist check-ups, there are many additional measures that can protect children’s teeth. These really all come down to one thing; avoiding added sugar. So …
As well as regular brushing of teeth and dentist check-ups, there are many additional measures that can protect children’s teeth. These really all come down to one thing; avoiding added sugar. So … The more obvious additional health and safety concerns include the following:
The more obvious additional health and safety concerns include the following: This guide was brought to you by the childcare team at
This guide was brought to you by the childcare team at 
 In this, the first of two new posts relating to the very youngest of children, we’re looking at teething, including when it usually happens and what to do about it as a parent or carer. Teething can be stressful for parents and a painful time for babies, so it’s important to read the signs correctly and act accordingly.
In this, the first of two new posts relating to the very youngest of children, we’re looking at teething, including when it usually happens and what to do about it as a parent or carer. Teething can be stressful for parents and a painful time for babies, so it’s important to read the signs correctly and act accordingly. Most babies are born with no teeth showing at all. However, there are exceptions and it’s reasonably common to be born with one or more milk teeth already visible. In total, babies will have a total of 20 milk teeth; 10 in the upper jaw and 10 in the lower. These are already there at birth as they will have grown during the embryonic stage. However, they are hidden within the gums in most cases.
Most babies are born with no teeth showing at all. However, there are exceptions and it’s reasonably common to be born with one or more milk teeth already visible. In total, babies will have a total of 20 milk teeth; 10 in the upper jaw and 10 in the lower. These are already there at birth as they will have grown during the embryonic stage. However, they are hidden within the gums in most cases. Teething can cause babies pain and discomfort during the 8 days in which each tooth moves from under the gum to erupting through it. Apart from the obvious signs of the tooth erupting and perhaps a bluey-grey eruption cyst colouration in the gums, symptoms of teething include:
Teething can cause babies pain and discomfort during the 8 days in which each tooth moves from under the gum to erupting through it. Apart from the obvious signs of the tooth erupting and perhaps a bluey-grey eruption cyst colouration in the gums, symptoms of teething include: There are a number of ways parents and carers can help babies and toddlers through their teething. One or more of the following may help:
There are a number of ways parents and carers can help babies and toddlers through their teething. One or more of the following may help: According to the NHS, there is no evidence that commercially-available teething gels (including homeopathic ones) are effective, so they recommend that non-medical options like those above should be tried first.
According to the NHS, there is no evidence that commercially-available teething gels (including homeopathic ones) are effective, so they recommend that non-medical options like those above should be tried first. When the time is right (usually by the age of 6) the milk teeth will start to shed. Normally, this is done in a particular order: first the two lower front teeth and the two upper front teeth will fall out (these are called the central incisors). Next to fall are the lateral incisors, then the first molars, the canines and finally the second molars.
When the time is right (usually by the age of 6) the milk teeth will start to shed. Normally, this is done in a particular order: first the two lower front teeth and the two upper front teeth will fall out (these are called the central incisors). Next to fall are the lateral incisors, then the first molars, the canines and finally the second molars.

 Less likelihood of developing cardiovascular disease including hyperlipidemia1;
Less likelihood of developing cardiovascular disease including hyperlipidemia1; Higher physical activity and physical fitness levels are associated with improved cognitive performance (e.g., concentration, memory) among students.3
Higher physical activity and physical fitness levels are associated with improved cognitive performance (e.g., concentration, memory) among students.3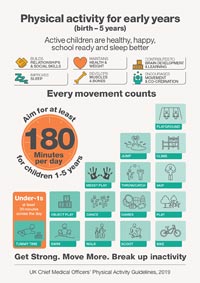
 Knowing how important it is, we take exercise very seriously at Treetops Nursery in Willesden. However, we ensure that it’s always fun and exciting, so that children enjoy it, naturally. Physical movement and active play are all part of
Knowing how important it is, we take exercise very seriously at Treetops Nursery in Willesden. However, we ensure that it’s always fun and exciting, so that children enjoy it, naturally. Physical movement and active play are all part of 