
 Even newborn babies should be encouraged to be active, in order to learn and develop their abilities through interaction and play. At this age, this is achieved largely through activities known collectively as Tummy Time. This is an incredibly important tool for their early development. Tummy Time pretty much describes the essence of the activities — i.e. time spent awake and active on their tummies during their first year.
Even newborn babies should be encouraged to be active, in order to learn and develop their abilities through interaction and play. At this age, this is achieved largely through activities known collectively as Tummy Time. This is an incredibly important tool for their early development. Tummy Time pretty much describes the essence of the activities — i.e. time spent awake and active on their tummies during their first year.
There’s a very good reason why high quality nurseries, pre-schools and other early years professionals encourage under-fives to learn largely through play. It’s the most natural way that they will develop physically and socially, learn about the world and develop skills like communication, language and problem-solving along the way. The beauty of learning through play is that it’ll also be great fun for the child, so won’t seem like a chore at all. It’s no different when children are babies and that’s where, for them, Tummy Time also comes in.
The Benefits of Tummy Time
You are your baby’s favourite playmate! Babies, particularly newborns, totally rely on their parents for play as well as for everything else. Tummy Time should be a part of that.
 It helps them to build physical strength, particularly in their upper body, and helps them achieve various developmental milestones.
It helps them to build physical strength, particularly in their upper body, and helps them achieve various developmental milestones.- Encouraging them to lift their head regularly will strengthen a baby’s neck. That’s important because their head is rather heavy for them when they’re first born and an otherwise weak neck will be a potential safety risk if not strengthened. They need to learn to control its position.
- Raising themselves onto their arms whilst lifting their head will take this a step further to increase strength in arm muscles, shoulders, core, back and torso generally.
- Doing all of this will also begin to nudge them towards becoming more mobile and coordinated as they improve their fine and gross motor skills.
- As babies get more used to Tummy Time, it will also give them more access to new sensory experiences as they can increasingly explore the world, suitable safe objects and textures around them.
 Another important benefit of Tummy Time is that it helps babies avoid conditions like positional plagiocephaly (otherwise known as ‘flat head syndrome’) and positional torticollis (i.e. a twisted neck) because it allows them to change position more often.
Another important benefit of Tummy Time is that it helps babies avoid conditions like positional plagiocephaly (otherwise known as ‘flat head syndrome’) and positional torticollis (i.e. a twisted neck) because it allows them to change position more often.
Safety note: babies should only be on their tummies when playing and only ever under close supervision. They should sleep on their backs, as it is safer for them and reduces the chance of SIDS. So, it’s important not to let them nod off when playing on their tummies.
Example Activities
Tummy Time can include a variety of activities, each of which will help the baby develop those new skills and physical strength. Initially start with shorter sessions, for example 1-2 minutes and later 2-5 minutes at a time. Increase this gradually as they build up strength. By the time they’re 3 months of age, they should be doing Tummy Time for a minimum of an hour, split up into smaller sessions, over the course of the day.
Up to 3 months of age:
 You can lie the baby on their tummy (while awake of course) on a soft blanket or rug on the floor. Get down low so you can interact with them and play games like peek-a-boo at their level.
You can lie the baby on their tummy (while awake of course) on a soft blanket or rug on the floor. Get down low so you can interact with them and play games like peek-a-boo at their level.- Alternatively he/she could lie across your lap with you supporting his/her stability with a helping hand and laying against you for extra support …
- … or even position him/her on their belly on top of yours, so you’re face-to-face.
- In any of these positions, you can ensure that you keep the baby safe while you encourage them to prop themselves up on their hands, elbows or arms and lift their heads, even if only fleetingly initially. A rolled-up blanket can help as support and to give them reassurance.
- Another great Tummy Time position at this age is threading your hand and lower arm horizontally underneath their length, so you support their weight lengthwise from underneath, rather like you’re carrying them. Their limbs can hang down either side of your supporting arm (so they’re a little like a lion lying along a branch in a tree). You must, however, support their head and neck with your other hand/forearm. This position will give the baby the opportunity to take turns in supporting their own head and limbs, so strengthening muscles and developing motor skills etc.
3 to 6 months:
- From the age of 3 months, you can try to encourage greater control from the baby by tempting them with toys and rattles. You can even move these around a little to encourage greater motor control like reaching out, following the direction of movement with their head position, as well as giving them the opportunity to practise and improve their visual tracking.
From 6 to 9 months:
 Encourage the baby to support their own weight on their hand and arms (almost like a ‘push-up’ kind of position) for short periods. This can initially be done by helping to support them with a hand, lifting them under their chest or tummy. They’ll soon catch on and help to push themselves up and support their own head more and more.
Encourage the baby to support their own weight on their hand and arms (almost like a ‘push-up’ kind of position) for short periods. This can initially be done by helping to support them with a hand, lifting them under their chest or tummy. They’ll soon catch on and help to push themselves up and support their own head more and more.- Soon enough you’ll notice that they can pass a toy from one hand to the other.
- At this stage, they should also start to be able to roll sideways from the tummy position, in either direction, going from tummy to back and reverting to their tummy position again.
- Toys can be used to encourage them during these activities, so they practise reaching out and swivelling bodily to grab them. It’s like a full upper-body workout!
- Before long, your baby will be able to sit unaided, using their own arms for support.
- Soon thereafter they’ll begin to crawl (usually around 7-9 months of age). Once they’re achieving this, there’s no real need to continue with Tummy Time exercises although spending some time on their tummy will continue to benefit them and build strength and motor skills etc. while they’re playing.
Then the real fun begins! Before you know it, they’ll begin to stand on their own two feet, supporting their own weight while holding on for support. Walking will be the next major milestone thereafter, on their amazing journey of life.
Are You Looking for an Outstanding Nursery in Willesden, or near Willesden Green, Harlesden or Kensal Green?
Tummy Time is all part of the excellent childcare services available to our youngest babies at Treetops Nursery in Willesden. As well as being a nursery for babies, we offer the highest quality weekday childcare for children up to the age of 5 and aim to get every one of them ‘school-ready’ by the time they leave us. If you are looking for outstanding nurseries in Willesden, or near Willesden Green, Harlesden or Kensal Green, please get in touch while places are still available — we’d love to hear from you and show you around:



 Less likelihood of developing cardiovascular disease including hyperlipidemia1;
Less likelihood of developing cardiovascular disease including hyperlipidemia1; Higher physical activity and physical fitness levels are associated with improved cognitive performance (e.g., concentration, memory) among students.3
Higher physical activity and physical fitness levels are associated with improved cognitive performance (e.g., concentration, memory) among students.3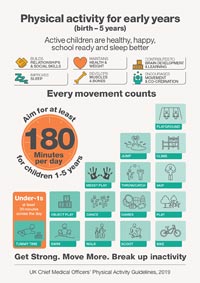
 Knowing how important it is, we take exercise very seriously at Treetops Nursery in Willesden. However, we ensure that it’s always fun and exciting, so that children enjoy it, naturally. Physical movement and active play are all part of
Knowing how important it is, we take exercise very seriously at Treetops Nursery in Willesden. However, we ensure that it’s always fun and exciting, so that children enjoy it, naturally. Physical movement and active play are all part of 